Debugging & Optimization
Troubleshooting Workflow
Typically, when troubleshooting problematic areas in positioning, follow this process:
- Beacon link connectivity: If not connected, positioning will not work at all. Bidirectional packet reception rate should be stable at 85% or above.
- Beacon link ranging: When bidirectional packet reception rate is normal, if ranging error is large, possible causes include:
- Fixed obstructions between beacons: As long as the obstruction is some distance from the beacon, the impact on positioning is usually minor.
- Beacon coordinate errors: These must be corrected, otherwise significant positioning errors will be introduced.
- No obvious obstruction: For example, mounting on walls or metal surfaces may cause severe multipath effects, greatly impacting positioning.
- Beacons installed incorrectly: If surrounding beacon links also show abnormal ranging, they may be mixed up. You can confirm by checking the flashing lights.
- Beacon coordinate errors: Coordinate errors should be controlled within 5% of the beacon distance, and within 2% for one-dimensional areas; otherwise, transitions between areas may have issues.
- Beacon-to-tag signal reception: In a given area, you should always receive signals from surrounding beacons. If no signals are received, positioning performance will definitely degrade.
- Tag parameter issues:
- Height above ground: Should be close to the actual tag usage height. The greater the error, the greater the impact on positioning.
- Height noise: Represents uncertainty in the vertical direction. If the tag typically operates between 1~2m, set the height to 1.5m and noise to 0.5m.
- Acceleration: Set according to the mobility of the target. Higher acceleration means lower delay but more jitter.
- Smoothing window: Uses data from several recent points for smoothing, introducing fixed delay. Larger window means smoother trajectory but greater delay.
- Constraint area settings: If constraint areas deviate significantly from reality, errors may increase, as this introduces incorrect assumptions.
- Relative position between multiple maps: Pay special attention to the relative coordinates between maps. If incorrect, it is equivalent to having beacons with coordinate errors, which greatly affects positioning.
- Tag hardware issues: If most other tags are normal, it may be an individual hardware problem. For battery-powered tags, check for low battery.
- Low computer performance: Low battery or insufficient computer performance may cause software lag and abnormal effects.
Checking Beacon Link Status
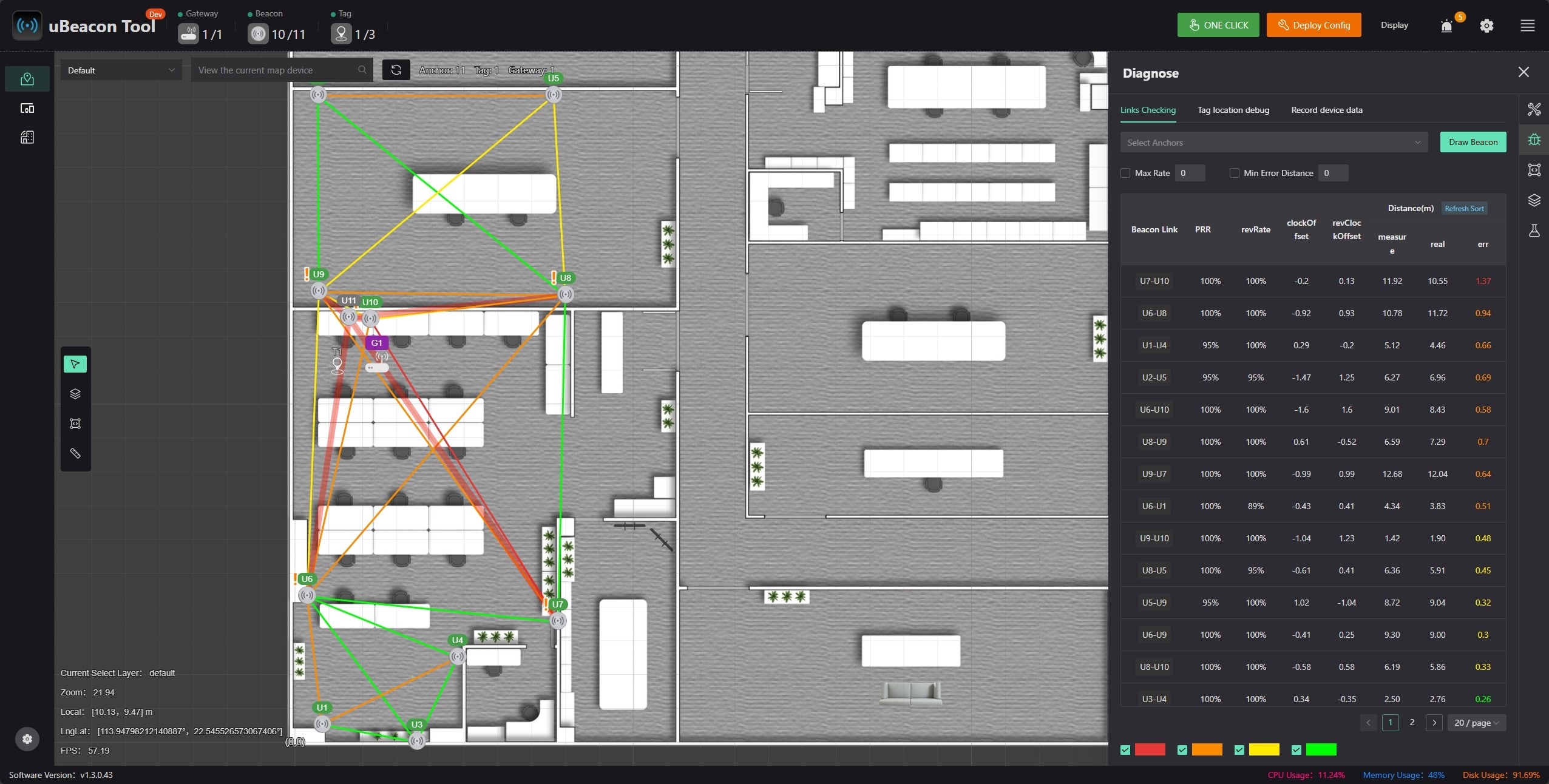
A beacon with an exclamation mark indicates it has unconnected links.
Red semi-transparent gradient lines indicate unconnected links.
The color of the lines between beacons indicates ranging error—the redder, the greater the error.
On the right is detailed link information, including bidirectional packet reception rate and ranging data.
Checking Beacon-to-Tag Signal Reception
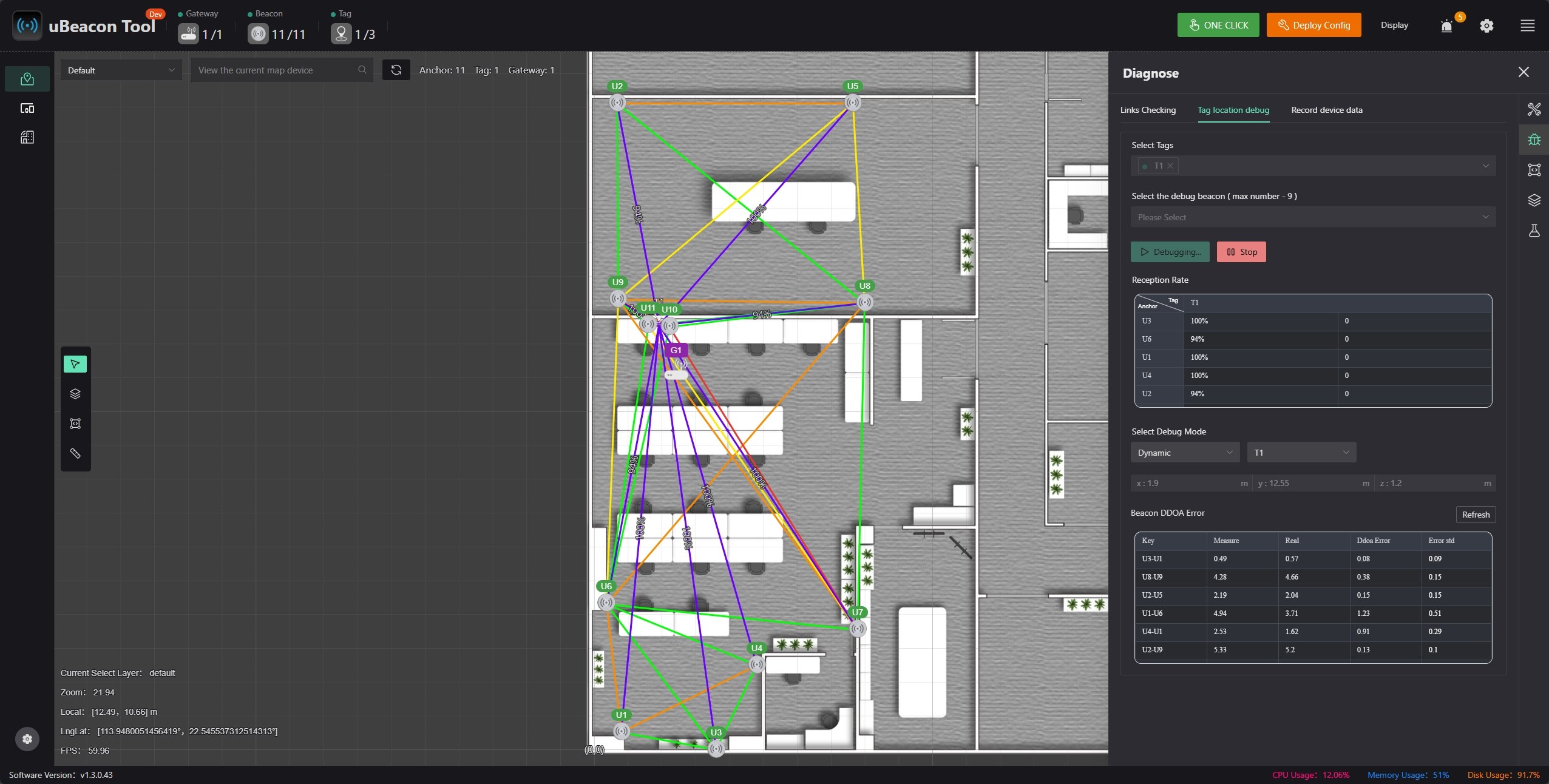
Switch to the tag positioning debug tab, select the beacon to observe, and start debugging.
Normally, if there are no other errors and packet reception rate is normal, positioning should be normal. However, anomalies may occur; you can check the ddoa error to further determine which beacon may have issues. Possible sources include:
- Obstructions between the tag's current position and the beacon
- The beacon's location is prone to multipath effects
- Other beacon-related error sources
Checking Tag Parameters
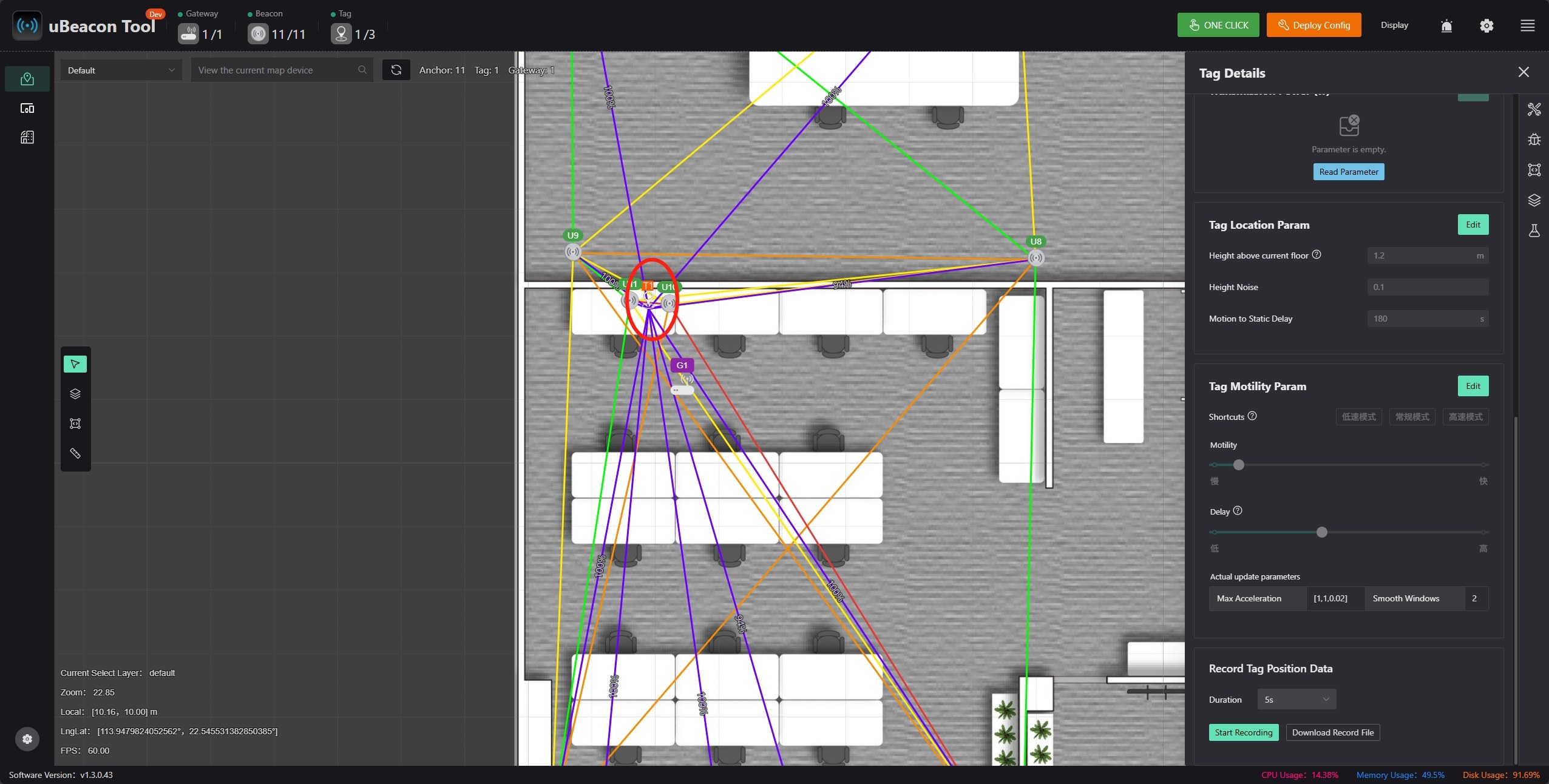
Click the tag icon on the diagram; you can set tag parameters in the information panel on the right.
Performance Optimization Methods
After completing the above troubleshooting, if results are still unsatisfactory, you can further optimize as follows:
- Optimize tag placement: For personnel positioning, helmet form > wristband form > badge form
- Optimize beacon placement:
- The higher the beacon, the less signal obstruction between beacon and tag
- The closer the length-to-width ratio is to 1, the better the effect
- Within communication range, the greater the distance between beacons, the smaller the relative error and the better the positioning
- Add more beacons: In theory, higher beacon density yields higher positioning accuracy